Adding sports into your daily life is one of the simplest approaches to enhance your general well-being. Beyond simply physical fitness, engaging in sports activities impacts mental health and emotional health, serving as a powerful tool for stress relief and mental clarity. As more human beings become aware of the benefits of keeping an active lifestyle, sports are rising as a central part of daily routines. Whether it’s heart health, diabetes prevention, or boosting mental health, sports play a pivotal role in creating a balanced and healthy life.
From aggressive sports to simple regular physical activity, the advantages extend far beyond just fitness benefits. They foster discipline, improve focus, and provide therapeutic effects that help control stress and improve mental health. When you add regular sports into your daily routine, it keeps your body fit and also acts as a holistic approach to promote a healthy mind and spirit.
By integrating sports into regular physical activity, individuals can experience improved fitness, decreased stress, and a healthier life. Different sports have different social and psychological benefits.
The Role of Sports in Weight Control
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), approximately 41.5% of adults in the United States are classified as obese. The rise in global obesity rates has increased the importance of physical activity in weight management and health has become more apparent than ever. Sport is vital in combating obesity by burning calories, improving metabolism, and fostering an active lifestyle.
Individuals who participate in sports can efficiently burn calories, build muscle, and shape their bodies without the monotony of conventional physical activity routines. Regular physical activity for individuals is a strong means for the prevention of diseases and for nations is a cost-effective method to improve public health across populations. Activities such as soccer, swimming, basketball, and tennis combine cardio and strength training, making them effective calorie burners. The intensity of physical activities in sports aids in fat loss and promotes cardiovascular health, which is crucial in managing weight-related issues.
Additionally, sport provides a comprehensive approach to weight management by supplementing healthy eating habits and improving overall fitness. Regular sports participation leads to achieving an ideal body weight, as burning calories and building muscle combine to help individuals achieve and maintain their desired physique. This approach prevents obesity and contributes to a lifestyle both dynamic and satisfying.
Compared to traditional physical activity, sports are more active and fun and can increase motivation and participation. Whether as part of a fitness routine or an enjoyable physical activity, sport also promotes mental health, health benefits, and emotional well-being, offering an effective and sustainable way to manage weight. Through participation with continued access, sport can significantly reduce the risk of obesity and promote a healthier lifestyle.

Reducing Hypertension Through Sports
According to the NIH, approximately 47.3% of adults in the United States have hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a serious health condition that can lead to stroke, heart attack, and other cardiovascular diseases. Fortunately, regular sports participation is one of the most effective ways to manage and reduce the risk of hypertension or high blood pressure. Physical activity helps improve blood pressure by improving cardiac function, increasing circulation, and improving overall heart health benefits.
Doctors consistently recommend incorporating sports and other forms of physical activity into daily activities as part of hypertension and high blood pressure management. Regular physical activity, such as team-based activities like swimming, running, cycling, or basketball, also helps lower blood pressure by strengthening the heart, allowing blood to flow more efficiently and with less effort. This reduction in workload on the heart leads to healthier blood pressure levels over time. when you start playing team sports, it starts boosting your strategy-making ability. The WHO emphasizes that engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity each week can help reduce the incidence of high blood pressure.
The cardiovascular benefits of physical activity are profound. Physical activity helps reduce the stiffness of blood vessels, increasing blood flow, which directly affects blood pressure control, improves mental health, and increases physical health. In addition, physical activity and weight reduction are important in reducing the risk of hypertension, as a healthy weight can significantly reduce blood pressure.
Lowering Cholesterol With Physical Activity
Cholesterol, a fatty substance in the blood, can pose serious risks to heart health when levels are too high. Regular involvement in sports and physical activity has proven to be one of the most effective and natural ways to reduce cholesterol levels and promote the overall well-being of the heart. Not as body physical activity not only improves heart health but also helps to regulate body fat levels, making it an integral part of a healthy person’s lifestyle.
Engaging in sports like running, swimming, cycling, and even playing team sports helps to increase high-density lipoprotein (HDL), commonly referred to as the “good” cholesterol, period-lowering low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or “bad” cholesterol. The psychological benefits of playing team sports as youths may spill over into adulthood. This balance improves cardiovascular health and reduces the risk of heart disease. For example, maintain excellent cholesterol profiles due to the intense and consistent physical activity they engage in, showing how an active lifestyle can positively impact cholesterol management.
For sedentary individuals, sports provide an accessible and enjoyable way to manage cholesterol. Even moderate exercise can make a big difference. Physical activity incorporated into daily and weekly routines helps burn body fat, increase metabolism, and improve blood circulation and mental health, all of which contribute to a healthy body fat mass. Conversely, a lack of physical activity can lead to weight gain and high LDL cholesterol, increasing the risk of heart complications. The goal of the WHO Global action plan on physical activity is to reduce physical inactivity by 15% by 2030. Research suggests that physical inactivity during adolescence carries over into adulthood
Improved Blood Circulation from Sports
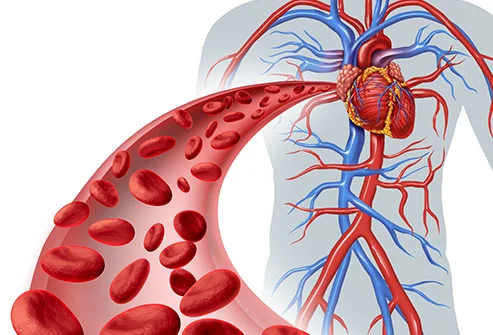
According to American Heart of Association, regular physical activity is associated with a 20-30% reduction in the risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks and strokes. Engaging in sports and physical activity plays an important role in increasing blood pressure and supporting cardiovascular health. Regular exercise stimulates the heart, improving its efficiency and improving its ability to circulate blood throughout the body. This process increases oxygenation, providing vital organs and muscles receive the oxygen they need to function optimally.
One of the key health benefits of sports is the strengthening of the heart muscle. Activities like running, swimming, cycling, and other aerobic exercises boost heart function by increasing capillary density, allowing for better blood flow and nutrient delivery. Over time, the heart becomes more efficient at pumping blood, which helps lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, such as heart attacks.
Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to poor circulation, which can lead to issues such as blood clots, atherosclerosis, and even heart disease. Without regular exercise, blood flow slows down, reducing oxygen flow to muscles and organs. Playing sports combats this by improving circulation and making blood vessels softer and stronger.
Aerobic exercise in particular is very beneficial for cardiovascular function. They increase the heart rate and encourage more blood flow and oxygen to the cells. This improved flow of oxygen helps reduce fatigue, increase endurance, and improve overall performance. Exercise also promotes the growth of new blood vessels, restoring circulation and supporting long-term cardiovascular health.
Strengthened Immune System Through Sports
Regular participation in sports and exercise increases physical fitness and strengthens the immune system, making the body more resistant to diseases. Sports exposure stimulates immune functions including the production of vital white blood cells and protects against infection.
Exercise has a direct effect on the immune system by increasing blood pressure. This allows white blood cells to circulate more efficiently, allowing them to better recognize and fight infection. Research by Sport England shows that people who engage in regular physical activity are less likely to suffer from infections like colds or flu. Immunity goes a long way, reducing the chances of common illnesses like the common cold and flu.
In addition to increasing white blood cell production, sports promote detoxification. Sweating helps the body remove toxins, bacteria, and waste from the blood, contributing to a healthy overall immune system. This natural process boosts the body’s immune system and maintains an internal balance.
Another health benefit of exercise is the regulation of body temperature, which plays a role in preventing harmful infections and boosting mental health. Body temperature rises during exercise, creating a less favorable environment for bacteria and viruses to thrive, further strengthening the immune system.
Muscle Strength and Coordination Through Sports

Playing sports provides significant benefits in muscle strength, organization, and memory. Unlike traditional exercise, sport provides an active and functional way to grow and proper muscle workout, using the body’s natural movements to feed the body all work well-being. By playing sports, you gain lean muscle mass and burn fat simultaneously. National guidelines recommend Australian adults do 2 ½ to 5 hours of moderate-intensity physical activity, or 1 ¼ to 2 ½ hours of vigorous-intensity physical activity each week, or an equivalent combination.
Playing sports increases muscle strength and coordination through a process called neuromuscular programming. It involves communication between the nervous system and muscle fibers to provide muscle control, reaction time, and efficiency. While engaged in sport, the body performs many complex reactions, contributing to muscle memory and efficiency. Over time, this repetitive practice strengthens muscle connections, improving motor skills and muscle tone.
While exercise is good for targeting muscles and building tone and strength, sport often offers a more advanced approach. Playing sports like football, basketball, and tennis uses multiple muscle groups simultaneously, making the whole body more coordinated and workmanlike. These tasks require rapid changes in direction, balance, and agility, coordinating and developing a proper muscle workout in ways that isolated exercises won’t.
Sports Models of Muscle Growth
- Swimming: engages the whole body, develops lean muscles, and improves overall coordination through the strokes and resistances from the water.
- Martial Arts: Increases muscle strength and coordination through complex movement, balance, and technique.
- CrossFit: Combines weight lifting, aerobic exercise, and high-intensity training to improve strength and coordination in various muscle groups.
Stronger bones
Taking part in sports not only strengthens your muscles but also your bones. During sports, you put stress on your bones with high power and strength movements; this, in turn, increases your bone density which results in stronger bones. For example, unlike normal walking, running while playing puts extra load or stress on your bones. In order to withstand this increased load stress, the bones adapt and become denser. If you continue to take part in sports, your bones keep becoming stronger and denser due to continuous stress. As we grow old our bone density keeps on decreasing. Indulging in sports might be the easiest way to maintain good bone density and remain strong with advancing age.
Bone Strength and Density from Sports
Playing sports is an effective way to increase bone density and strength, providing a natural solution to maintain good bone health throughout life. Regular physical activity, especially weight-bearing and high-impact team sports, plays an important role in skeletal turnover and age-related bone loss.
Playing sports helps to strengthen the bones by putting physical stress on the bones. Bones respond to the forces of exercise by becoming stronger and stronger. This process, known as bone turnover, involves the formation of new bone tissue in response to mechanical stress induced by moderate-intensity physical activity, such as running, jumping, and resistance training with increased loads on bones that stimulate bone-forming cells (osteoblasts) produced, increasing both bone density and strength.
The natural process of bone remodeling begins with the application of physical pressure during exercise. As bones undergo this stress, they undergo a new process in which old cartilage is replaced by new, stronger bone. This adaptive process requires a balance between bone resorption (breakdown of older bone marrow) and bone formation. Regular sports practice ensures that bone formation exceeds resorption, increasing bone density and strength over time. Team sports are best practices to improve public health across populations.
Benefits of Sports for Bone Health
Certain sports are particularly beneficial for improving bone health due to their weight-bearing and impact. Examples are:
- Running: A high-impact activity that strengthens bones in the lower body through repetitive stress.
- Basketball: There are jumps and quick changes of direction, which build bone strength in the legs and spine.
- Exercise: Several exercises and team sports strengthen bones throughout the body.
- Weight Lifting: Engages the skeletal system through resistance training, and increases bone density and strength.
Incorporating team sports into your routine is a powerful way to increase bone density and strength. Through physical stress and the natural process of bone turnover, playing sports promotes bone health and helps prevent age-related bone loss, weight-bearing activities, and high-impact physical activity interventions can provide significant health benefits in maintaining strong and healthy bones throughout life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the effect of physical activity and sports on general physiological health?
Physical activity and playing sports enhance cardiovascular health, boost immunity, improve muscle strength, aid in weight management, and reduce the risk of a chronic disease like diabetes.
How does physical health affect your daily life?
Good physical health boosts energy, improves mood, enhances productivity, reduces stress, and helps prevent illness, allowing for a more active, fulfilling daily life.
Why is exercise important in everyday life?
Exercise and team sports improve overall health by strengthening muscles, boosting mood, reducing stress, helping to gain lean muscle mass, and helping prevent diseases, making it crucial for maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
What are the positive and negative effects of sports?
Playing sports positively improves fitness, mental health, and social skills. However, negatives include injury risks, overexertion, cardiovascular disease, and stress from competition.
How can sports affect mental health?
Playing sports positively impacts mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and depression, boosting mood, improving sleep, and fostering social connections, leading to overall better emotional well-being.
What are the health benefits of playing sports and games?
Playing sports improves cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles and bones, enhances coordination, reduces obesity risk, boosts mental health, and promotes better sleep and social interaction.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only, and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More







