Asthma is a lifetime chronic condition characterized by wheezing, breathlessness, and cough. While inhalers are an immediate treatment for asthma attacks, cases arise where they aren’t available.
Let’s explore how to stop asthma wheezing without an inhaler.
Asthma Symptoms
Asthma symptoms include:
- Wheezing
- Shortness of breath
- Chest tightness
- Coughing
Asthma triggers include allergens, cold air, exercise, and stress – Therefore, successful management requires information on asthma symptoms, their triggers, and how to manage them.
Managing Asthma Wheezing Without an Inhaler
Suffering from an asthma attack with no inhaler? – Here’s what can help:
Controlled Breathing Techniques
- Pursed-Lip Breathing: Inhale slowly through your nose and exhale through pursed lips, opening airways for long – making breathing easier. (American Lung Association)
- Diaphragmatic Breathing: Belly breathing is breathing down into your abdomen. Place one hand on the chest and another on the abdomen – inhale slowly through the nose, allowing the abdomen to rise, and then exhale. (World Health Organization)
Find a Calm, Comfortable Position
Stress and anxiety worsen asthma symptoms. Try being calm, sit upright or slightly forward to open your airways. Do not lie down, it’ll worsen breathing.
Warm, Humid Environment
Warm, humid air liquefies mucus and reduces wheezing – so, a hot shower and steam inhalation can heat nasal passages.
Stay Hydrated
Moistening the throat and airways with warm fluids, like herbal tea or honey water, is soothing. Hydration helps thin out the mucus, making breathing easier.
Avoid Triggers
Asthma triggers include allergens, smoke, fumes, strong odors, and cold air. Moving to a cleaner environment helps. Weather conditions, such as cold air and humidity can impact asthma symptoms.
Here’s how to manage asthma in various weather conditions:
1) Cold Weather
Cold can tighten airways, causing wheezing and breathlessness – so:
- Cover Nose and Mouth: Use a scarf or mask as a filter to warm the air before inhaling.
- Stay Indoors in Extreme Cold: Avoid outdoor activities in extreme cold.
2) Humidity
Humidity triggers asthma with the proliferation of mold, dust mites, and other allergens in the air – while low humidity dries out the airways. To manage humidity levels:
- Use a Dehumidifier: Indoor humidity should be between 30-50%.
- Avoid Outdoor Activities on Humid Days: Stay indoors during humid days, minimizing asthma attacks.
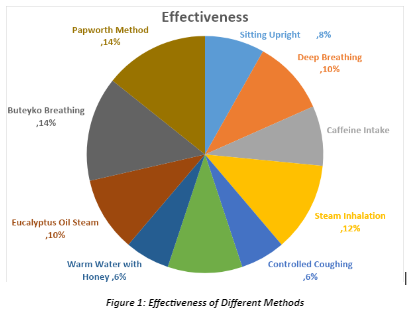
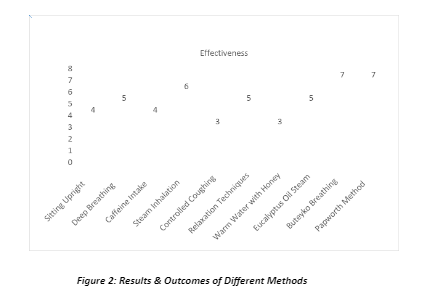
Comparison of Non-Inhaler Asthma Wheezing Relief
| Method | Effectiveness | Ease of Use | Speed of Relief | Possible Drawbacks |
| Sitting Upright | Moderate | Very Easy | Very Easy | Immediate low effect on severe attacks |
| Deep Breathing | Moderate | Easy | Within minutes | Requires practice and attention |
| Ingestion of Caffeine | Moderate | Easy | 15-30 minutes | Increased shakiness in the body. |
| Steam Inhalation | High to Moderate | Moderate | 5-10 minutes | Requires preparation, burn hazard |
| Controlled Coughing | Low to Moderate | Moderate | Varies | Worsened symptoms if done wrong |
| Relaxation Techniques | Moderate | Moderate | 5-15 minutes | Requires practice, may not assist in severe cases |
| Warm Water with Honey | Low to Moderate | Easy | Easy 10-20 minutes | Ineffective for severe symptoms |
| Eucalyptus Oil Steam | Moderate | Moderate | 15-20 minutes | Potential allergic reaction, strong smell |
| Buteyko Breathing | Moderate to High | Difficult | Varies | Requires training and consistent practice |
| Papworth Method | Moderate to High | Difficult | Varies | Requires professional instructions |
Age-Specific Considerations
– How to stop asthma wheezing for different ages:
| Method | Adults | Kids | Older Adults |
| Sitting Upright | Effective | Effective | Effective |
| Slow, Deep Breathing | Effective | Effective | Effective |
| Staying Calm | Important | Important | Important |
| Removing Triggers | Important | Important | Important |
| Warm, Caffeinated Beverages | Effective | Not recommended for children | Use with caution due to potential heart issues |
| Steam Inhalation | Effective | Effective but requires supervision | Effective, but may require assistance |
| Pursed-Lip Breathing | Effective | Not recommended for young children | Effective |
| Consuming Honey | Effective | Effective but consult the pediatrician first | Effective, but use with caution |
| Using Eucalyptus Oil | Effective but use caution | Not recommended without pediatrician approval | Effective, but use with caution |
| Relaxation Techniques | Effective | Effective but may need parental | Effective, but may require assistance |
Source: How to treat an asthma attack without an inhaler WebMD.
Statistical Approches:
Comparative Analysis of Asthma Across Different Age Groups
| Category | Children | Adults | Older Adults(65+years) |
| Prevalence | 6.5% US | 85 in the US | Increases with age and weight |
| Gender Differences
|
Boys 7.0% > Girls 5.4% | Women 10.8% > men 6.5% | – |
| Asthma Attacks | 38.7% experienced an attack within the past year | 39.6% experienced an attack within the past year | – |
| Healthcare Utilization | High levels of ED visits and hospitalized patients under the age of 4 | 15.7% were work-related asthma attacks | – |
| School/Work Impact | Missed more school days | Greater impact on women, specifically with adult-onset asthma | – |
| Mortality | Rare in children | Uncommon in adults | Highest in older adults |
Is Asthma Genetic?
Evidence shows that some people are more predisposed to asthma due to genetics. These genes, most of which are involved in the host’s immune responsiveness and airway inflammation, have a strong influence on the development and severity of asthma.
– Key Genes And Their Impact
Immune Response Genes and Airway Inflammation Genes: These genes are major determinants of asthma development – they mediate a physiologic response to allergens and other asthma triggers.
Polymorphisms Affecting Asthma:
- Il333, Gsdmb, and Tslp: Variants in these genes predispose to asthma.
- Rage, Il17a, Il17f, Fosbb, Corin, Spp1, CXCL5: Products of genes modulating the degree of inflammation and maintenance of the integrity of respiratory tract epithelial barrier.
Importance of Genetic Awareness
Knowing specific gene variations that make populations vulnerable to asthma is important. Such genetic marker identification done earlier contributes to the timely establishment of risk controls; reducing the incidence and severity of asthma attacks. This genetic awareness is a critical move toward individual strategies for the management and prevention of asthma attacks.
Conclusion
Wheezing and asthma are difficult to manage without an inhaler, but not impossible if know the right techniques. Being aware of the weather, its impact, and how to manage asthma attacks without an inhaler can be helpful.
The above-mentioned measures are not a substitute for medical treatment. If the asthma gets worse, seek immediate medical attention – and it’s necessary to determine an appropriate management plan
By incorporating the following tips, and a few other ways to tackle asthma symptoms – you can improve the quality of your life, reducing the chances and severity of asthma attacks.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health-related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More