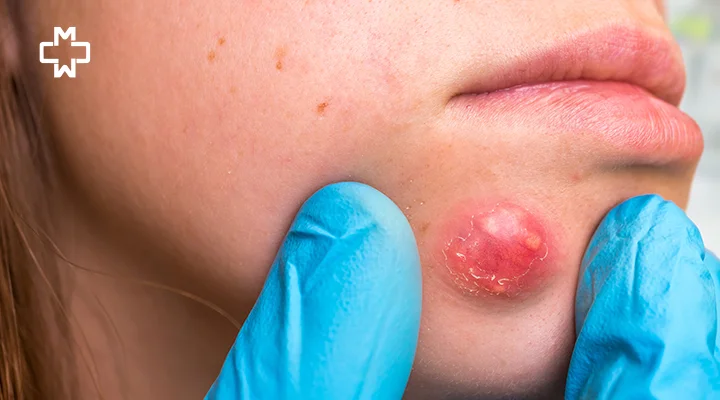
What is a Boil?
A boil, also known as a furuncle, is a common skin infection that begins in a hair follicle or oil gland. It typically starts as a red, tender lump that gradually fills with pus as the infection progresses. Boils can occur anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, thighs, and buttocks.
Types of Boils
There are 3 main types of boils:
- Furuncles: These are the most common type of boils and usually occur in hair follicles.
- Carbuncles: Carbuncles are clusters of furuncles that form a deeper and more severe infection.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: This chronic skin condition causes recurrent boils in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits and groin.
What Causes Boils?
- Bacterial Infection: Boils are primarily caused by bacterial infections, most commonly by the Staphylococcus aureus bacteria. These bacteria enter the body through cuts, breaks in the skin, or hair follicles, leading to the formation of boils.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene can increase the risk of developing boils. Failure to regularly cleanse the skin can allow bacteria to accumulate, increasing the likelihood of infection.
- Compromised Immune System: Individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, diabetes, or undergoing chemotherapy, are more susceptible to bacterial infections, including boils.
- Friction or Irritation: Friction or irritation to the skin caused by tight clothing, shaving, or prolonged pressure can damage hair follicles or oil glands, creating an entry point for bacteria and increasing the risk of boil formation.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can impair the body’s ability to fight infections, making individuals with diabetes more prone to developing boils.
- Obesity: Obesity is associated with an increased risk of developing boils due to factors such as poor circulation, skin folds that trap moisture and bacteria, and compromised immune function.
- Close Contact: Close contact with individuals who have boils or carriers of Staphylococcus aureus bacteria can increase the likelihood of bacterial transmission and subsequent boil formation.
What Are The Symptoms of Boils?
The common symptoms of boils include:
- Red, swollen bump
- Pain or tenderness
- Formation of pus
- Skin around the bump becomes warm
- Fever in severe cases
How To Get Rid of a Boil Overnight?
Getting rid of a boil overnight is not practically possible – However, there are remedies that can help these boils heal much faster.
Applying warm compresses over boils for 20 minutes during the day – And applying antibiotic cream, castor oil, or neem oil overnight to help draw out the infection and allow the body to heal.
How Long Do Boils Last?
The duration of a boil varies depending on its size and severity. In most cases, a boil will resolve on its own within 1-2 weeks. However, seeking prompt treatment and following the recommended remedies can help expedite the healing process.
How to Treat Boils?
In addition to home remedies, medical treatment for boils may include:
- Incision and drainage: A healthcare professional may need to make a small incision to drain the pus from the boil.
- Antibiotics: In severe cases or for recurrent boils, antibiotics may be prescribed to eliminate the bacterial infection.
Home Remedies for Boils
These home remedies can help with expediting the healing process:
- Warm Compresses: Apply a warm compress to the boil for 10-15 minutes several times a day to promote drainage and relieve pain.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antibacterial properties, tea tree oil can help fight the infection. Dilute tea tree oil with a carrier oil and apply it to the boil.
- Turmeric Powder: Turmeric has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. Mix turmeric powder with water to form a paste and apply it to the boil.
- Epsom Salt Bath: Soaking in a warm bath with Epsom salt can help draw out the pus and reduce inflammation.
- Castor Oil: Apply castor oil directly to the boil and cover it with a bandage. Castor oil helps reduce inflammation and promotes healing.
- Neem Oil: Neem oil has antibacterial properties that can help fight the infection. Apply neem oil directly to the boil several times a day.
- Tridax Daisy: Crush tridax daisy leaves to extract the juice and apply it to the boil. Tridax daisy has antimicrobial properties that can aid in healing.
- Aloe Vera: Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the boil to soothe the skin and promote healing.
- Raw Onion: Place a slice of raw onion over the boil and cover it with a bandage overnight. Onion has antimicrobial properties that can help fight the infection.
- Devil’s Horsewhip Extract: This herbal extract has antimicrobial properties that can aid in healing. Apply devil’s horsewhip extract to the boil several times a day.
- Proper Hygiene: Keep the affected area clean and dry to prevent further infection and promote healing.
When to See a Doctor?
It’s essential to consult a doctor if:
- The boil is accompanied by a fever
- The boil is larger than a pea
- Multiple boils appear
- The boil is located on the face, near the eyes, or on the spine
Frequently Asked Questions
Are boils contagious?
Yes, boils can be contagious, especially if they are caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Direct contact with the pus from a boil or with items contaminated by the pus can spread the infection.
Can stress cause boils?
Stress doesn't directly cause boils, but it can weaken the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infections like those that cause boils.
What do boils look like?
Boils typically start as red, tender bumps on the skin. As they develop, they may fill with pus, become larger, and eventually rupture, draining pus and blood.
How fast does tea tree oil work on boils?
The effectiveness of tea tree oil on boils can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience relief within a few days of consistent application, while for others, it may take longer to see noticeable improvement.
What foods should you avoid if you have boils?
To help prevent or manage boils, it's recommended to avoid foods that are high in sugar and processed carbohydrates, as these can contribute to inflammation and weaken the immune system. Additionally, reducing intake of dairy and fatty foods may also be beneficial for some individuals.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only, and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More