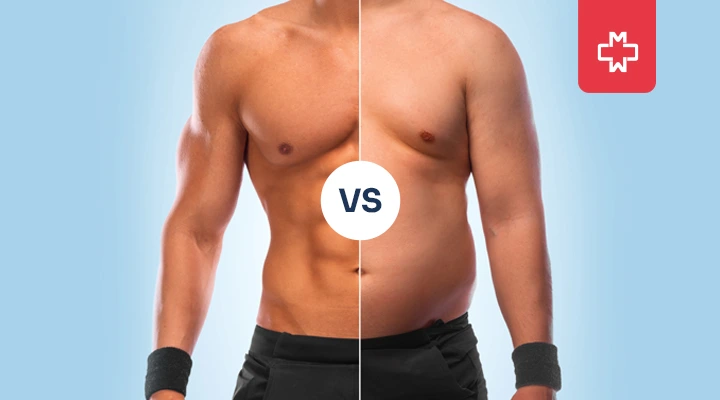
Ever wondered about the secret story your body tells? Sarcopenic Obesity is like a hidden character in this tale, making things more concerning than just weight and looks. Think of it as a puzzle where your muscles and fat have a unique relationship.
Ready to dive into a story that’s not about numbers but about understanding yourself better? Join us on a journey that explores everything you should know about Sarcopenic Obesity, helping you discover a simpler, healthier way of living.
What is Sarcopenic Obesity?
Sarcopenic Obesity is a health condition characterized by the simultaneous presence of two major issues: Muscle loss (sarcopenia) and excessive body fat.
In simpler terms, it’s a situation where the body experiences a decline in muscle mass while also gaining an unhealthy amount of fat. This combination poses unique challenges to overall health and well-being – going beyond the concerns that are typically associated with either muscle loss or obesity alone.
How Does Sarcopenic Obesity Differ from General Obesity?
To truly grasp the complexities of Sarcopenic Obesity, one must differentiate it from its more familiar counterpart – General obesity.
While both involve an increase in body fat, Sarcopenic Obesity in older adults takes it a step further, incorporating the additional challenge of muscle wasting. In essence, it’s a double-edged sword, each facet worsening the impact of the other on your health and well-being.
What Causes Sarcopenic Obesity?
Sarcopenic Obesity, a multifaceted health concern, does not have a single origin; instead, it emerges from a complex connection of various factors that influence our body’s composition.
Understanding the diverse causes behind Sarcopenic Obesity is quite important for both prevention and effective intervention.
- Sedentary Lifestyle:
Lack of physical activity not only promotes fat accumulation but also contributes significantly to the gradual loss of muscle mass. The human body, designed for movement, undergoes adverse changes when confined to a sedentary routine.
- Poor Nutrition:
The saying “you are what you eat” is particularly true when it comes to Sarcopenic Obesity. Insufficient protein intake, coupled with imbalances in essential nutrients, can hinder muscle maintenance and repair. Additionally, a diet high in processed foods and sugars may develop fat deposition, worsening the complexities of this condition.
- Aging Process:
Aging brings about natural changes in body composition, characterized by a decline in muscle mass and an increase in body fat. Sarcopenic Obesity often intensifies with age, as the body’s ability to regenerate muscle tissue diminishes, and metabolic processes become less efficient.
- Chronic Diseases:
Certain medical conditions can act as catalysts for Sarcopenic Obesity. Chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disorders, and inflammatory conditions may accelerate the wasting of muscles while promoting fat storage.
- Hormonal Changes:
Hormones play a major role in regulating muscle mass and fat distribution. Imbalances, often associated with aging, menopause, or endocrine disorders, can tip the scales towards Sarcopenic Obesity.
- Genetic Predisposition:
Our genetics contribute to the risk of developing Sarcopenic Obesity in older adults. Some individuals may be inherently more susceptible due to genetic factors that influence muscle metabolism, fat storage, or the body’s response to exercise.
- Inflammation and Oxidative Stress:
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress are key players in the development of Sarcopenic Obesity. These processes not only accelerate muscle breakdown but also contribute to insulin resistance and fat accumulation. Addressing the inflammatory aspects of this condition is pivotal for effective management.
Diagnostic Criteria For Sarcopenic Obesity
Diagnosing Sarcopenic Obesity demands a complex approach that goes beyond traditional weight assessments. This condition requires a comprehensive evaluation to unravel its complexities.
Here’s an in-depth exploration of the diagnostic criteria for sarcopenic obesity, highlighting the sophisticated methods employed by healthcare professionals in identifying and understanding sarcopenic obesity in older adults:
- Body Composition Analysis: Utilize advanced tools like DEXA, BIA, and CT scans for precise muscle and fat assessment.
- Functional Assessments: Gauge muscle impact on daily life through strength tests and mobility evaluations.
- Laboratory Tests: Identify physiological drivers with blood tests for insulin resistance, inflammation, and hormonal imbalances.
- Physical Activity History: Assess exercise habits and daily activities to contextualize muscle and fat changes.
- Clinical Examination: Hands-on examination detects signs like muscle atrophy and changes in body composition.
- Patient Symptomatology: Consider patient-reported symptoms for a comprehensive clinical profile.
- Assessment of Coexisting Conditions: Evaluate comorbidities like diabetes to inform a holistic diagnostic approach.
Treatment For Sarcopenic Obesity
Addressing Sarcopenic Obesity requires a multidimensional approach that targets both muscle loss and excessive fat accumulation.
Here’s a concise overview of various treatment options designed to restore balance and promote overall well-being:
- Resistance Training: Engaging in targeted resistance exercises helps rebuild muscle mass and strength. Incorporating activities like weightlifting or resistance band exercises enhances muscle function, mitigating the impact of Sarcopenic Obesity.
- Protein-Rich Diet: Adequate protein intake is crucial for muscle maintenance and repair. A diet rich in lean proteins supports muscle health, reducing the risk of further muscle wasting associated with sarcopenic obesity in older adults.
- Balanced Nutrition: A well-rounded and nutritionally balanced diet is essential for overall health. Ensuring the right mix of nutrients, vitamins, and minerals supports not only muscle health but also helps regulate fat metabolism.
- Cardiovascular Exercise: Incorporating cardiovascular activities, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, contributes to overall fitness and aids in managing excess body fat.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): In cases where hormonal imbalances contribute to Sarcopenic Obesity, hormone replacement therapy may be considered. Balancing hormones can positively impact muscle mass and fat distribution.
- Medications: Certain medications may be prescribed to address specific aspects of Sarcopenic Obesity, such as those targeting metabolic function, inflammation, or insulin resistance. Medications are often tailored to individual health needs.
- Physical Therapy: Customized physical therapy programs can enhance mobility, flexibility, and overall physical function. Physical therapists work collaboratively to address muscle weaknesses and improve functional abilities.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopting a healthy lifestyle is fundamental in managing Sarcopenic Obesity. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, and avoiding habits detrimental to muscle health, such as excessive alcohol consumption.
- Nutritional Counseling: Working with a nutritionist provides personalized guidance on dietary choices, ensuring optimal nutrient intake for muscle health and overall well-being.
- Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up: Continuous monitoring of progress and periodic follow-up with healthcare professionals are crucial components of Sarcopenic Obesity management. This allows for adjustments to treatment plans based on individual responses and changing health needs.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of Sarcopenic Obesity is very important when aiming for a healthy body. At Manhattan Medical Arts, we’re not just here to shed light on the complexities of this condition; we’re your partners in achieving holistic well-being.
Whether it’s personalized treatment plans or expert guidance, our commitment extends beyond information – it’s about empowering you to reclaim control over your body composition and overall health.
Sarcopenic Obesity may be a puzzle, but with the right pieces in place, a healthier, stronger you is within reach.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only, and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More