Strained your hamstring and itching to get back in action? Whether you’re an athlete chasing goals or a weekend warrior, a hamstring strain can put the brakes on your progress. But don’t worry—quick and effective recovery is within reach. In this blog, we’ll disclose the secrets of how to heal a hamstring strain fast. Say goodbye to frustrating setbacks and hello to rapid relief. Get ready to bounce back stronger and faster with our essential tips for healing a hamstring strain swiftly and effectively. Your path to recovery starts here.
What is a Hamstring Injury?
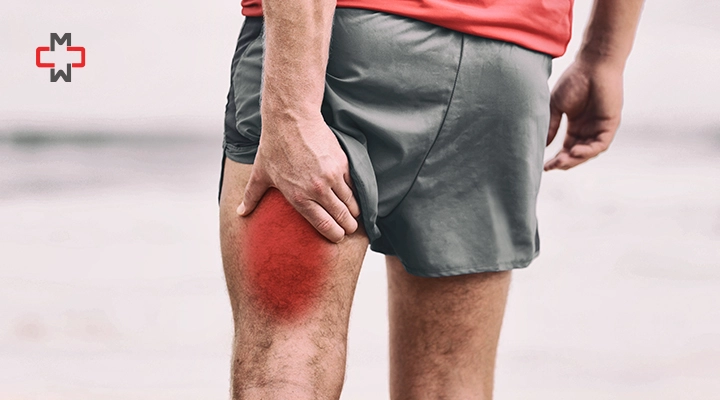
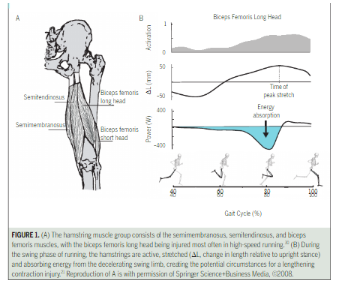
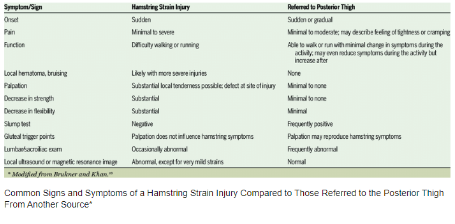
A hamstring injury involves damage to one or more of the three muscles located at the back of the thigh: the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus. These muscles are crucial for movement and stability in the legs. Hamstring injuries can vary in severity, from mild strains to complete tears. According to the NHS, hamstring strains are categorized into three grades:
Grade I (Mild): Minor muscle strain with slight discomfort.
Grade II (Moderate): Partial tear with more significant pain and swelling.
Grade III (Severe): Complete tear of the muscle or tendon, often requiring surgery.
Source: Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations for Diagnosis, Rehabilitation, and Injury Prevention
What Causes Hamstring Injury?
Hamstring injuries commonly occur due to:
- Overstretching: Rapid movements or overstretching of the muscle during activities like sprinting can cause strain.
- Overuse: Prolonged physical activity without adequate rest can lead to muscle fatigue and strain.
- Improper Warm-Up: Not warming up properly before physical activity can increase the risk of injury.
- Muscle Imbalance: Weakness or imbalance between the hamstrings and quadriceps can contribute to strain.
Source: Hamstring Strain Injuries: Recommendations for Diagnosis, Rehabilitation, and Injury Prevention
How Long Does a Pulled Hamstring Take to Heal?
The healing time for a pulled hamstring varies based on the injury’s severity:
- Grade I Strain: Mild hamstring strains can typically take 1-3 weeks to heal.
- Grade II Strain: This can take 4-8 weeks, depending on the extent of the tear.
- Grade III Strain: Often requires 3-6 months of recovery and may need surgical intervention.
What Makes a Hamstring Injury Worse?
Certain factors can exacerbate a hamstring injury:
- Premature Return to Activity: Resuming sports or exercise too soon can aggravate the injury.
- Inadequate Rehabilitation: Failing to follow a proper rehab program can lead to incomplete recovery and recurrence.
- Continued Stress on the Muscle: Persistent physical activity without sufficient rest can prevent healing.
- Improper Technique: Incorrect exercise techniques or movements can strain the muscle further.
How to Treat a Pulled Hamstring?
Effective treatment for a hamstring strain includes:
- Avoid activities that stress the hamstring. Rest is crucial for healing.
- Apply ice packs to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every 1-2 hours during the first 48 hours to reduce swelling and pain.
- Use an elastic bandage to compress the area and minimize swelling.
- Keep the injured leg elevated above heart level to reduce swelling.
- Over-the-counter pain medications, such as ibuprofen, can help alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Gradual stretching and strengthening exercises can aid recovery and prevent future injuries. It’s essential to follow a rehabilitation program and physical therapy exercises designed by a physical therapist.
- If your job is physically demanding, hamstring strain exercises can help you avoid issues.
When to See a Doctor?
You should seek medical attention if:
- Severe Pain: The pain is intense and does not improve with home treatment.
- Swelling: Significant swelling or bruising that does not subside.
- Inability to Walk: Difficulty or inability to bear weight on the injured leg.
- Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms persist or worsen despite self-care measures.
A visit to a healthcare professional can ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. If necessary, they may recommend imaging tests, such as an MRI, to assess the extent of the severe hamstring injuries.
Frequently Asked Questions
No schema found.– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health-related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More