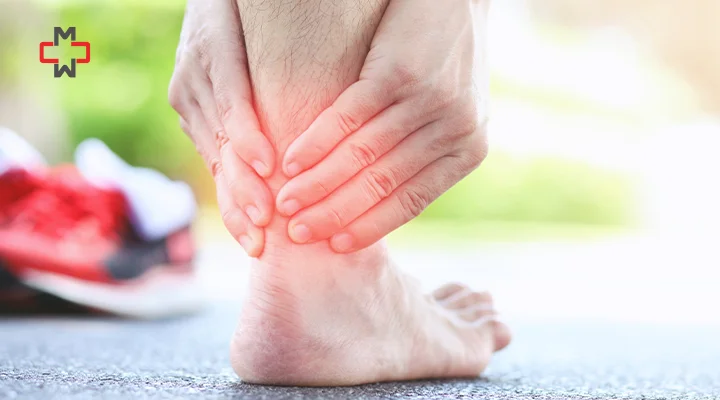
Have you ever experienced a sharp pain at the back of your heel, particularly after physical activity?
This might be a sign of Achilles tendonitis, a condition common among athletes and physically active individuals.
Today’s blog will explore what Achilles tendonitis is, its types, causes, and diagnosis – along with answering the most inquired question: ‘How to cure Achilles tendonitis fast?’
What is Achilles Tendonitis?
The Achilles tendon is a strong band of tissues that connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. When this tendon becomes inflamed or irritated, it leads to a condition known as Achilles tendonitis. This condition can range from mild to severe, causing pain and discomfort, especially during physical activity.
Types of Achilles Tendonitis
There are two main types of Achilles tendonitis:
- Noninsertional Achilles Tendonitis: This type involves fibers in the middle portion of the tendon and tends to affect younger, active people.
- Insertional Achilles Tendonitis: This type involves the lower portion of the heel, where the tendon attaches to the heel bone. It can occur at any age, even among the less active.
Ways to Cure Achilles Tendonitis Fast
Listed below are the most effective ways that can help cure an Achilles tendonitis fast:
- Rest and Immobilization: Avoid activities that aggravate the condition and consider using crutches to reduce pressure on the tendon.
- Applying Ice and Heat Therapy: Ice packs can help reduce inflammation, while heat therapy can promote blood flow and healing.
- Orthotic Devices and Footwear: Specialized inserts or shoes can provide support and reduce strain on the Achilles tendon.
- Stretching and Strengthening Exercises: Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility and reduce the risk of further injury.
What Causes Achilles Tendonitis?
Various factors can contribute to the development of Achilles tendonitis, including:
- Overuse: Engaging in repetitive physical activities, such as running or jumping, can strain the Achilles tendon.
- Tight or Weak Muscles: Tight calf muscles or weak leg muscles can increase the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis.
- Improper Footwear: Wearing shoes that do not provide sufficient support or cushioning can strain the Achilles tendon.
- Sudden Change in Physical Activities: Increasing the intensity or duration of physical activities too quickly can also strain the Achilles tendon.
- Age and Degeneration: As we age, our Achilles tendon can degenerate and can be easily injured.
- Previous Injury: A history of Achilles tendonitis or other foot and ankle injuries can increase the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis.
- Excessive Pronation: Overpronation, or excessive inward rolling of the foot, can strain the Achilles tendon.
- Flat Feet: People with flat feet or fallen arches may be more prone to developing Achilles tendonitis.
Diagnosis
Proper diagnosis of Achilles tendonitis typically involves a physical examination, where your doctor will look for signs of swelling, tenderness, or a palpable lump along the tendon.
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound or MRI, may also be used to confirm the diagnosis.
Achilles Tendonitis Treatment
Achilles tendonitis treatment usually involves a combination of rest, ice, physical therapy – and in some extreme cases, medication or surgery.
Here are some common treatment options:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Avoid activities that worsen the condition and consider switching to low-impact activities.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can help improve flexibility and strength in the affected tendon.
- Orthotic Devices: Achilles tendinitis medical devices such as shoe inserts or orthotic devices can offer support and reduce strain on the Achilles tendon.
- Medication: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged tendon.
When to See a Doctor?
It is necessary to consult a doctor if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or difficulty walking. Seeking instant medical attention can help prevent further damage and speed up the recovery process.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does Achilles tendonitis feel like?
Achilles tendonitis typically feels like a sharp pain or stiffness at the back of the heel. It may worsen during physical activity and improve with rest.
How long does Achilles tendonitis last?
The duration of Achilles tendonitis varies depending on its severity and how it's managed. With proper treatment, mild cases may improve in a few weeks, while more severe cases may take several months to heal.
What exercises should not be done with Achilles tendonitis?
Exercises that put excessive strain on the Achilles tendon should be avoided, such as high-impact activities like running or jumping, as well as exercises that involve sudden or repetitive ankle movements.
What worsens Achilles tendonitis?
Achilles tendonitis can worsen with activities that strain the tendon, such as running, jumping, or walking uphill. Improper footwear, sudden increases in activity levels, and insufficient rest can also worsen the condition.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health-related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More