What Are Chromosomes?
Each cell in the human body contains a nucleus within, which possesses DNA molecules that are packaged as a thread-like structure called Chromosomes. The term chromosome comes from the Greek words for color (chroma) and body (soma). Females have 2 X chromosomes. Males have one X chromosome and one Y chromosome. Human chromosomes are made using DNA that is coiled multiple times around a protein called histones, which is responsible for supporting its structure.
If body cells are not in the process of dividing, the human chromosomes are not visible at all, not even under a microscope. However, when a cell is dividing that is when sex chromosomes become visible under a microscope since that is when the human DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) gets much more tightly wrapped. Hence, everything that researchers know today about human chromosomes was actually learned through conducting observations during the process of cell division. The only human cells that do not contain pairs of chromosomes are reproductive cells, or gametes, which carry just one copy of each chromosome.
A chromosome map is divided into two sections, also known as the two “arms”; and the centromere is the constriction point for each chromosome that causes this division. Both these arms are differently sized, so the shorter one is called the “P arm”, while the longer one is called the “Q arm”. Human chromosomes vary in number and shape among living organisms. Most bacteria have one or two circular chromosomes. Humans, along with other animals and plants, have linear chromosomes. Among the 24 chromosomes in humans, the Y chromosome is special because it has a lot of repeating parts. Scientists are studying it to learn more about human health and diseases. (National Institutes of Health)
What Are Homologous Chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are basically two human chromosomes that are paired together – generally inherited from both parents, one from each. For instance, 2 copies of the X chromosome within a single cell will be known as homologous chromosomes.
In terms of biology, homologous chromosomes are paired human chromosomes. The similarities are that they possess identical centromere location, loci (gene position), gene sequence, and chromosomal length. Having said that, even if their genetic sequence and loci are exactly the same; there will definitely be differences in alleles.
How Many Sex Chromosomes Do Humans Have?
Chromosomes are always found to be paired with one another – and there are 23 pairs of human chromosomes for each cell present in our body, which makes it a total of 46 sex chromosomes. This total number of human chromosomes is inherited, since half of these two chromosomes come from the father, while the other half come from. Typically, biologically female individuals have two X chromosomes (XX) while those who are biologically male have one X and one Y chromosome (XY).
Source: (National library of medicine)
What Are Chromosomes Made Of?
Being an intertwined structure found inside the nucleus of a cell – A sex chromosome is made up of proteins and DNA that are organized into genes. Each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Where In The Human Cells Are Chromosomes Located?
Found in the nucleus of a cell, sex chromosomes are structures that are responsible for carrying long pieces of DNA. Being the building block and the base for the human body, DNA is responsible for holding genes together.
Homologous Chromosomes Vs Sister Chromatids
It is essential to understand the difference between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes. Sister chromatids have their utilization in cell division such as cell replacement. While homologous chromosomes are capable of being used in the reproductive cells, to help make new babies.
Sister chromatids are genetically the same, being identical copies of one another specifically created for cell division. In fact, the term sister chromatid is only used during the parts of cell division when the structures are in that X shape, or when a centromere connects the two copies.
Also, a pair of homologous chromosomes consists of two non-identical copies of a chromosome, one from each parent. Here are a few more differences between sister chromatids and homologous chromosomes:
– Function
Homologous chromosomes allow random segregation of chromosomes and genetic recombination during metaphase I.
Sister chromatids allow random segregation of chromatids and chromosomal crossover during metaphase II of meiosis and metaphase of mitosis.
– Joining
Homologous chromosomes do not stick together, they exist in pairs. Sister chromatids are joined together by their centromere.
– Genetic Composition
Homologous chromosomes may contain the same or different alleles of the same gene. Thus, the gene sequence is not identical at all times.
Sister chromatids contain identical gene sequences throughout the chromatids except in the chromosomal crossover.
– Appearance
Homologous chromosomes appear in metaphase I of meiosis I. Sister chromatids are formed during the DNA replication in the S phase of interphase.
– Number of DNA Strands
Homologous chromosomes are composed of four DNA strands.
A single sister chromatid is composed of a single DNA strand.
– Separation
Homologous chromosomes are segregated during anaphase I of meiosis I.
Sister chromatids are separated from their centromere during anaphase II of meiosis II and the anaphase of mitosis.
During Which Three Phases Are Individual Chromosomes No Longer Visible?
There are three phases during which the sex chromosomes are no longer visible:
i) Interphase
ii) Cytokinesis
iii) Telophase
Interphase is the stage of the cell cycle during which a cell becomes prepared to be divided. It is the longest phase of the cell cycle that takes almost 23 hours to complete in human cells.
In telophase, the chromosomes decondensed back after the nuclear division has occurred.
And in cytokinesis also, the cytoplasmic division takes place after telophase and therefore, the chromosomes are not visible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do humans have 22 or 23 chromosomes?
Humans have 23 pairs of sex chromosomes, totaling 46 chromosomes.
What gender has 22 chromosomes?
All humans, regardless of gender, have 22 pairs of autosomes. The 23rd pair determines gender.
Do we have 46 or 47 human chromosomes?
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes. Having 47 sex chromosomes usually indicates genetic traits like Down syndrome.
What gender is a YY chromosome?
A YY chromosome combination is not viable in humans. The typical male two-chromosome patterns are X and one Y chromosome.
What are autosomes?
In humans, each cell normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46. Twenty-two of these pairs, called autosomes, look the same in both males and females.
How do sex chromosomes behave during the different phases of cell division in mitosis?
During mitosis, chromosomes condense in prophase, align at the cell's equator in metaphase, separate into sister chromatids in anaphase, and de-condense as two nuclei form during telophase.
What is a centromere?
A centromere is part of linear chromosomes that link sister chromatids and where spindle fibers attach during cell division, ensuring accurate distribution of sex chromosomes to daughter cells.
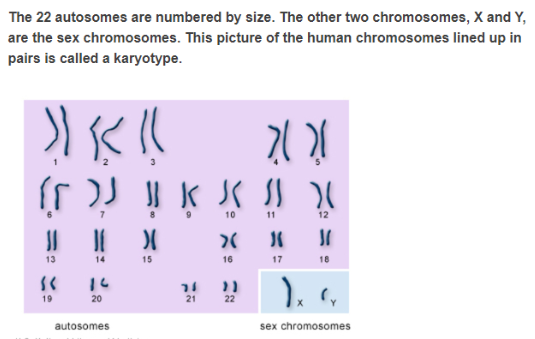
What is karyotype?
A karyotype is the complete set of human chromosomes lined up in a cell, organized and visualized under a microscope. It helps in identifying chromosomal abnormalities, determining sex, and studying genetic disorders.
– Disclaimer –
This blog is for informational & educational purposes only, and does not intend to substitute any professional medical advice or consultation. For any health related concerns, please consult with your physician, or call 911.
-
About The Author
Dr. Syra Hanif M.D.Board Certified Primary Care Physician
Dr. Syra Hanif is a board-certified Primary Care Physician (PCP) dedicated to providing compassionate, patient-centered healthcare.
Read More